iDeyFind: An AI-assisted customer-driven solution for modern e-commerce
Abstract: In a predominantly product-driven e-commerce industry, a purely customer-focused e-commerce model that allows online customers to create personalized requests for the products or services they want would be complementary and directly improve the overall efficiency of e-commerce.
A lot of customers who visit multiple e-commerce platforms in search of specific products or services usually know exactly what they want. The current product-driven e-commerce model does not account for the unavailability of products for this kind of customer. In this very common case, the e-commerce platforms lose customers when the products they need are not available.
We propose a customer-driven e-commerce solution that provides a framework for online customers to create requests for the products or services that they need, connect with vendors around them who can deliver the products or services and deal with them directly.
This not only ensures that customers can get products and services at highly competitive prices, It gives vendors a chance to make sales without spending on advertising. It has the potential to optimize revenue on existing e-commerce platforms by capturing the customers who would have bounced after being unable to find their desired products. For companies of all sizes, this model has the potential to bring digital transformation and optimization benefits to traditional procurement processes.
The integration of AI serves to simplify the process of creating parameters for the product and service requests. These parameters are then used as data points to calculate percentage matches when the vendors begin to respond to the requests, enabling the customers to make data-driven decisions on which vendor to deal with.
Finally, the entire parameters agreed upon by customer and vendor can be put into an agreement and electronically signed by both parties, creating a basis for trust where each party is bound by their obligations in the contract. The contract also serves as a basis for the return of products or termination when there is a breach by either party.
Introduction
Imagine wanting a new pair of sneakers but not having to visit a store to buy them. Instead, you open your phone, browse an online store, choose the perfect pair, and place an order. Within days, they arrive at your doorstep. This is e-commerce as we know it, e-commerce is the exchange of goods and services over the internet.
For over 30 years, e-commerce has transformed how people shop. Instead of walking through aisles in a physical store, customers can browse thousands of products online, compare prices, read reviews, and make purchases —all from the comfort of their homes. Businesses, both big and small, use e-commerce to reach customers worldwide, breaking the limitations of traditional brick-and-mortar stores.
In an attempt to replicate the experience of traditional brick-and-mortar stores for online users, online shopping platforms operate an e-commerce model that we can describe as product-driven. This e-commerce model largely depends on the availability of products in stock hence the transactions on these platforms usually originate with vendors uploading product images, adding some description and setting a price.
Online shopping platforms like Amazon, eBay, and Shopify operate the product-driven ecommerce model and have made it easier than ever to find and buy almost anything— clothes, electronics, books, and even groceries. Many of these platforms use algorithms to suggest products based on browsing history, making shopping a more personalized experience.
But e-commerce isn't just about buying; it's also about selling. Many individuals and small businesses create online stores to sell handmade crafts, digital products, or even services. Platforms like Etsy and Shopify allow anyone with an idea and internet access to start a business with minimal upfront costs.
One of the biggest advantages of e-commerce is convenience. Unlike physical stores, online shops are open 24/7, and customers don't have to deal with crowds or long checkout lines. Additionally, e-commerce enables people in remote areas to access products they might not find locally.
However, e-commerce also comes with challenges. Online fraud, identity theft, and counterfeit products are risks shoppers must be aware of. That's why secure payment methods, trusted sellers, and customer reviews are essential when making online purchases.
Another major downside to product-driven e-commerce is the inefficiency of the conversion funnel, with top performing e-commerce platforms recording remarkably low conversion rates between 2% - 5% in contrast with walk-in retail stores which have much higher conversion rates between 20% to 40%.
We will examine the inefficiencies that exist in today's e-commerce and work through possible solutions to curb these inefficiencies and drive conversion rates.
Classification of e-commerce transactions
Modern e-commerce is unlimited in its scope, however transactions that take place online can largely be categorized as follows;
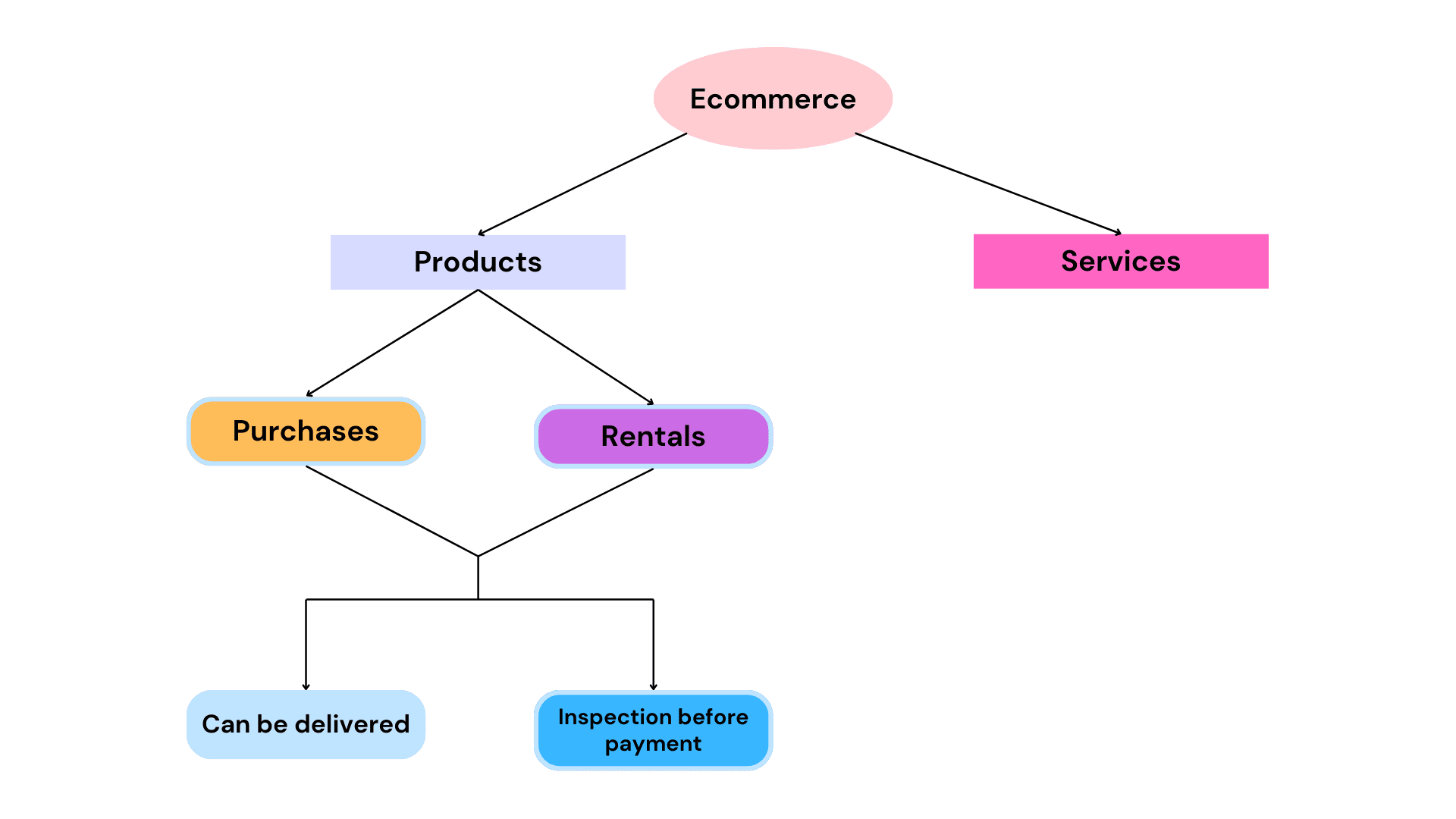
Products
As the name implies, this refers to tangible items both physical and digital, that can be sold in exchange for money or cryptocurrency. The basic process for buying products online typically involves browsing through various options that exist in the catalogue of the online stores and selecting the most preferred option(s).
- Purchases: A purchase happens when a customer desires to take full ownership of a product after payment is made, therefore they are required to pay the full amount corresponding to the value of the item and a service charge which the online store records as revenue.
- Rentals: A rental happens in a case where the customer desires to make use of a product for a specified period of time in hours, days, months or even years. In this case they do not have to pay the full value of the product and the amount they pay is usually a small fraction of the price of the item, with additional charges to account for depreciation, wear and tear, maintenance etc, depending on the market value of the item.
Classes of products
- Products that can be delivered: This class includes products whose description via pictures and specification on the online platform are sufficient to earn the trust and confidence of the customer, hence can be delivered without thorough inspection. Products in this category include household items, consumer electronics, and products within a price range that is relatively comfortable for the consumer. They usually come with warranty and can be returned easily if found to be defective.
- Products that require inspection before payment: These products usually have a higher price range compared to the previous class and in most cases cannot be practically purchased without an inspection. This class includes vehicles, real estate, heavy machinery, aircrafts, vessels, etc and requires the presence of a professional to carry out an inspection on both the facility and documentation.
Services
This encompasses various broad categories of services including household, professional, industrial, healthcare, hospitality etc. The prices and description of these services are usually displayed, a lot of detail is left out and there are usually no specific terms of engagement pertaining to the current transaction as it is difficult to capture these details with the traditional e-commerce model.
Examining the traditional product-driven e-commerce model
The internet gave rise to the traditional e-commerce model which has enabled businesses to advertise their products to online customers and make sales. This model focuses largely on products because every online sale using this model is based on advertising products in stock. In other words, customers can only buy what a store has in stock, and they often have to scout different online stores for availability, reviews and price comparison before making a final decision. Online stores often have to decide whether to cater to a wide audience or be niche focused. The general purpose online stores today often lose a large amount of traffic to smaller niche-focused online stores because they have competitive advantage by focusing on a particular niche. The downside of being niche focused is less traffic which is expected considering the fact that their customers are fewer.
Diagrammatic representation of the product-driven e-commerce model

Typical conversion funnel on traditional product-driven e-commerce platforms
There are various factors that determine whether a customer on an e-commerce platform will make a purchase;
- Intent to buy
- Purchasing Power
- Availability of products
- User experience
Conversion funnel KPIs in the Nigerian eCommerce market
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for the conversion funnel in the Nigerian eCommerce market include;
- Add-to-cart rate - 8.8%
- Cart abandonment rate - 90.7%
- Conversion rate - 0.8%
- Search rate - 69%
- Bounce rate from search - 80%
Identifying how traffic is lost on product-driven ecommerce platforms
- Cart abandonment: This accounts for about 8% of total traffic on e-commerce platforms.
- Bounce rate from search: This accounts for a whooping 55.2% of total traffic and is the largest loss of customers on e-commerce platforms today.
Introducing Customer-driven e-commerce
Customer-driven e-commerce is an e-commerce model that provides a framework for customers to create personalized requests for products and services, connect with vendors around them that can deliver the products and services and deal with them directly.
Diagrammatic representation of customer-driven e-commerce

Key terms and definitions:
- Requests: A request is a structured document containing a title, and parameters highlighting details of a product or service that a customer needs. A request can be for a product or service, it could also be a purchase or rental request. Users can create requests for products that can be delivered to them and products which would require inspection before payment.
- Parameters: Parameters are itemized details contained in a request, representing the user's need. Parameters for a product request include features the customer wants in the product, the condition of the product, budget, deadline, color preference, delivery preference and any additional information about the product. Parameters for service requests include the job description and qualification of the service provider, hourly, daily, or monthly rate depending on the nature of the engagement, and duration of the service.
- AI recommendations: AI generated recommendations are used to suggest product features based on the title of the request. They are also used to suggest qualifications and job descriptions for service requests.
- AI tokens: In order to generate AI recommendations, API requests are made to AI models. These API calls have cost implications and the service providers include terms of use mandating developers to prevent abuse of the service on their applications. The AI tokens are a means to control the use of AI recommendations on customer-driven e-commerce platforms using a prepaid subscription model where customers can choose to buy tokens from a range of bundle sizes. Each AI recommendation costs 1 token
- Proposals: A proposal is a structured document containing a vendor's response to a request, highlighting parameters that align with their product or service. The proposal also contains the vendor's quote or bid price. Vendors are able to see how closely their proposal aligns with the customer's request, represented by the percentage of parameters in the proposal that align with the parameters in the customer's request.
- Percentage match: This is a figure that represents the percentage of parameters in a vendor's proposal that align with the parameters in the customer's request
- Average bid price: This is the mean bid price of all vendors who have previously submitted proposals to a particular request. This metric is used to help vendors to finetune their prices before submitting their proposals.
- Average percentage match: The average percentage match represents the mean percentage match of all vendors who have previously submitted proposals to a particular request. This metric is used as a benchmark for vendors to compare the percentage match of their proposals to that of other vendors before submission.
- Transaction tiers: This is a metric used to classify transactions based on their sizes with upper and lower limits, allowing for fine-grained control, security, transparency, and restrictions on certain sizes of transactions.
- Proposal tokens: Vendors on customer-driven e-commerce platforms can be charged using a prepaid subscription model with a range of bundle sizes to choose from. Vendors are charged varying amounts of tokens to send their proposals depending on the tier of the transaction which is determined by the bid price contained in the proposal.
- Customer-vendor agreement: This is a contractual agreement between customers and vendors highlighting all the agreed upon parameters, including the price and other details of the transaction.
AI integration in customer-driven e-commerce
Customer-driven e-commerce thrives on AI for ease of use and effectiveness. The possibility is limitless but the immediately apparent application of AI in this e-commerce model includes;
- Feature recommendation:
- Sample image generation
- Price estimation
Benefits of customer-driven e-commerce
Customer-driven e-commerce holds benefits to the following participants
- Customers can get products and services at highly competitive prices.
- Vendors get a chance to make sales without spending on advertising
- Online Stores can optimize revenues by capturing customers who would have bounced after being unable to find their desired products
- Organizations of all sizes can bring digital transformation and efficiency to their manual procurement processes.
Conclusion
The customer-driven e-commerce model can be implemented in a standalone application or a plugin which can be used on existing product-driven e-commerce platforms. The essence of this documentation is to introduce core concepts and highlight its potential.
iDeyFind is pioneering the use of this e-commerce model in its suite of applications. The intricacies of the implementation may differ, but the core concepts remain the same across the board.
